Do Hammertoe Splints Do The Job
 Overview
Overview
A Hammer Toe can be flexible or rigid. Hammertoes often start out flexible and become rigid over time as your toe becomes accustomed to its crooked position. Flexible hammertoes are less serious than rigid hammertoes, as they can be easily diagnosed and treated in their initial stages. Flexible hammertoes are named as such because your affected toe still possesses some degree of movement.
Causes
Shoes that narrow toward the toe force the smaller toes into a bent upward position. This makes the toes rub against the inside of the shoe, and creates corns and calluses, aggravating the toes further. If the shoes have a high heel, the feet are forced forward and down, squeezing the toes against the front of the shoe, which increases the pressure on the toes and makes them bend further. Eventually, the toe muscles become unable to straighten the toe. 
Symptoms
People who have painful hammertoes visit their podiatrist because their affected toe is either rubbing on the end their shoe (signaling a contracted flexor tendon), rubbing on the top of their shoe (signaling a contracted extensor tendon), or rubbing on another toe and causing a painful buildup of thick skin, known as a corn.
Diagnosis
Hammertoes are progressive, they don?t go away by themselves and usually they will get worse over time. However, not all cases are alike, some hammertoes progress more rapidly than others. Once your foot and ankle surgeon has evaluated your hammertoes, a treatment plan can be developed that is suited to your needs.
Non Surgical Treatment
Try to find shoes that are soft, roomy, and comfortable and avoid tight shoes or shoes with high heels. A shoe repair shop may be able to stretch a small pocket in regular shoes to make room for the hammertoe. Have a professional pedicure. Sometimes a skilled manicurist can file down a painful corn. Follow your healthcare provider's instructions. Ask your provider what activities you should avoid and when you can return to your normal activities, how to take care of yourself at home, what symptoms or problems you should watch for and what to do if you have them. Make sure you know when you should come back for a checkup.
Surgical Treatment
If conservative measures fail to provide relief, or if your hammertoe is in advanced stages with rigidity and a significant amount of pain, surgery may be required. Some patients also require surgery if they have open sores or wounds related to their hammertoe. For patients who also suffer from bunions, a combined procedure may be appropriate, addressing both conditions within the same surgery. Recovery time will vary from patient to patient, depending on the extent of the surgical repair and other conditions that may also be present.
Hammer Toe Non Surgical Treatment
 Overview
Overview
Hammer toes are usually not a serious condition, but can become painful as the bent joint rubs against the inside of the shoe, causing irritation, corns, or calluses on the top of the middle joint or the tip of the toe. A Hammer toes may also cause occasional shooting pains throughout the toes or elsewhere in the foot. A hammertoe has a kink or contracture in its second joint--called the proximal interphalangeal joint--that causes the toe to bend upward in the middle, giving it a hammer-like appearance. The raised part of the toe often rubs on shoes, leading to the formation of corns or calluses. Usually hammertoe affects the smaller toes, causing pain and interfering with the ability to walk normally.
Causes
A person may be born with hammer toe or may develop it from wearing short, narrow shoes. Hammer toe can occur in children who outgrow shoes rapidly. Sometimes hammer toe is genetic and is caused by a nerve disorder in the foot. High heeled shoes are can also cause hammer toe. The reason for this is that the toes are not only bunched up, but the weight of the body is pushing them forward even further.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
The symptoms of a hammer toe include the following. Pain at the top of the bent toe upon pressure from footwear. Formation of corns on the top of the joint. Redness and swelling at the joint contracture. Restricted or painful motion of the toe joint. Pain in the ball of the foot at the base of the affected toe.
Diagnosis
Most health care professionals can diagnose hammertoe simply by examining your toes and feet. X-rays of the feet are not needed to diagnose hammertoe, but they may be useful to look for signs of some types of arthritis (such as rheumatoid arthritis) or other disorders that can cause hammertoe.
Non Surgical Treatment
Treating hammertoe involves straightening the toe, making tendons in the toes flexible again, and preventing the problem from returning. Some simple treatments include Soaking your feet every day in warm water, then stretching your toes and ankles by pointing your toes. Using over-the-counter pads, cushions or straps to decrease discomfort. Splinting the toe to keep it straight and to stretch the tendons of the foot. Exercising the toes Hammer toe to relax the foot tendons (a session with a physical therapist may help you get started with foot exercises). One simple exercise is to place a small towel on the floor and then pick it up using only your toes. You also can grasp at carpet with your toes or curl your toes up and down repeatedly. Wearing shoes that fit properly and give toes plenty of room to stretch out.
Surgical Treatment
If these non-invasive treatments don?t work, or if the joint is rigid, a doctor?s only recourse may be to perform surgery. During the surgery, the doctor makes an incision and cuts the tendon to release it or moves the tendon away from or around the joint. Sometimes part of the joint needs to be removed or the joint needs to be fused. Each surgery is different in terms of what is needed to treat the hammertoe. Normally after any foot surgery, patients use a surgical shoe for four to six weeks, but often the recovery from hammertoe surgery is more rapid than that. An unfortunate reality is that hammertoe can actually return even after surgery if a patient continues to make choices that will aggravate the situation. Though doctors usually explain pretty clearly what needs to be done to avoid this.
 Prevention
Prevention
How can I prevent hammer toe? Avoid wearing shoes that are narrow or don?t fit well. Also, don?t wear heels higher than 2 inches. Instead, choose shoes with a wide toe box that give you ? inch between the end of your longest toe and the inside tip of the shoe. Check often to make sure your child?s shoes fit, especially when he or she is having a growth spurt.
Is Hammer Toe Uncomfortable
 Overview
Overview
When a person has Hammer toe, the end of their toe bends downward and the middle joint curls up. Eventually, the toe gets stuck in a stiff, claw-like position. When the inside of your shoe rubs against a hammer toe, corns, blisters or calluses may form on top of the toe or on the bottom of your foot. This can make walking painful. You may also have pain in the joint where your big toe joins your foot. Hammer toe usually affects a person?s second toe (the toe next to the big toe), but it can affect other toes too.
Causes
Hammertoes are most common in women, and a big part of this is poor shoe choices, which are a big factor in the development of many foot problems. Tight toe boxes and high heels are the biggest culprits. Genetics certainly plays a role in some cases of hammertoes, as does trauma, infection, arthritis, and certain neurological and muscle disorders. But most cases of contracted toes are associated with various biomechanical abnormalities in how a patient walks. This causes the muscles and tendons to be used excessively or improperly, which deforms the toes over time.
 Symptoms
Symptoms
A hammer toe may be painful, especially when irritated by a shoe. All four toe conditions may cause cramps in the toes, foot and leg due to the abnormal function of the tendons in the foot. If a mallet toe has occurred, you are likely to suffer from a corn at the end of the toe. A hammertoe may cause a corn on the top of the toe. Infections Hammer toe and ulcers can also occur. In severe cases a mallet toe, trigger toe, claw toe or a hammer toe may create a downward pressure on the foot, which can result in hard skin and corns on the soles of the feet.
Diagnosis
The exam may reveal a toe in which the near bone of the toe (proximal phalanx) is angled upward and the middle bone of the toe points in the opposite direction (plantar flexed). Toes may appear crooked or rotated. The involved joint may be painful when moved, or stiff. There may be areas of thickened skin (corns or calluses) on top of or between the toes, a callus may also be observed at the tip of the affected toe beneath the toenail. An attempt to passively correct the deformity will help elucidate the best treatment option as the examiner determines whether the toe is still flexible or not. It is advisable to assess palpable pulses, since their presence is associated with a good prognosis for healing after surgery. X-rays will demonstrate the contractures of the involved joints, as well as possible arthritic changes and bone enlargements (exostoses, spurs). X-rays of the involved foot are usually performed in a weight-bearing position.
Non Surgical Treatment
You can usually use over-the-counter cushions, pads, or medications to treat bunions and corns. However, if they are painful or if they have caused your toes to become deformed, your doctor may opt to surgically remove them. If you have blisters on your toes, do not pop them. Popping blisters can cause pain and infection. Use over-the-counter creams and cushions to relieve pain and keep blisters from rubbing against the inside of your shoes. Gently stretching your toes can also help relieve pain and reposition the affected toe.
Surgical Treatment
Joint resection procedures involves removing part of one of the two small joints of the toe directly underneath where the digit is crooked. The purpose is to make room for the toe to be re-positioned flat or straight. Because hammer toes become rigid or fixed with time, removing the joint becomes the only option when the knuckle is stiff. Its important to understand that this procedure does not involve the joint of the ball of the foot, rather the a small joint of the toe. Medical terminology for this procedure is called a proximal interphalangeal joint arthroplasty or a distal interphalangeal joint arthroplasty, with the latter involving the joint closer to the tip of the toe.
Bunions All You Need To Know
Overview
 A bunion, or Hallux Valgus, is a foot deformity characterised by deviation of the bones around the big toe joint of the foot. As a result, there is a large exostosis or bony lump on the inside of the foot and the toe is pointed across towards the smaller toes. It is a common problem, more so in women and has been attributed to tight fitting footwear. This article will cover the basics of bunions, what it is due to, and what treatment is available.
A bunion, or Hallux Valgus, is a foot deformity characterised by deviation of the bones around the big toe joint of the foot. As a result, there is a large exostosis or bony lump on the inside of the foot and the toe is pointed across towards the smaller toes. It is a common problem, more so in women and has been attributed to tight fitting footwear. This article will cover the basics of bunions, what it is due to, and what treatment is available.
Causes
Many problems that occur in the feet are the result of abnormal pressure or rubbing. One way of understanding what happens in the foot due to abnormal pressure is to view the foot simply. Our simple model of a foot is made up of hard bone covered by soft tissue that we then put a shoe on top of. Most of the symptoms that develop over time are because the skin and soft tissue are caught between the hard bone on the inside and the hard shoe on the outside. Any prominence, or bump, in the bone will make the situation even worse over the bump. Skin responds to constant rubbing and pressure by forming a callus. The soft tissues underneath the skin respond to the constant pressure and rubbing by growing thicker. Both the thick callus and the thick soft tissues under the callus are irritated and painful. The answer to decreasing the pain is to remove the pressure. The pressure can be reduced from the outside by changing the pressure from the shoes. The pressure can be reduced from the inside by surgically removing any bony prominence.
Symptoms
The signs and symptoms of a bunion include a bulging bump on the outside of the base of your big toe, swelling, redness or soreness around your big toe joint, Thickening of the skin at the base of your big toe, Corns or calluses, these often develop where the first and second toes overlap, persistent or intermittent pain, restricted movement of your big toe. Although bunions often require no medical treatment, see your doctor or a doctor who specializes in treating foot disorders (podiatrist or orthopedic foot specialist) if you have persistent big toe or foot pain, a visible bump on your big toe joint, decreased movement of your big toe or foot, difficulty finding shoes that fit properly because of a bunion.
Diagnosis
Although bunions are usually obvious from the pain and unusual shape of the toe, further investigation is often advisable. Your doctor will usually send you for X-rays to determine the extent of the deformity. Blood tests may be advised to see if some type of arthritis could be causing the pain. Based on this evaluation, your doctor can determine whether you need orthopaedic shoes, medication, surgery or other treatment.
Non Surgical Treatment
When a bunion first begins to develop, take good care of your feet. Wear wide-toed shoes. This can often solve the problem and prevent you from needing more treatment. Wear felt or foam pads on your foot to protect the bunion, or devices called spacers to separate the first and second toes. These are available at drugstores. Try cutting a hole in a pair of old, comfortable shoes to wear around the house. 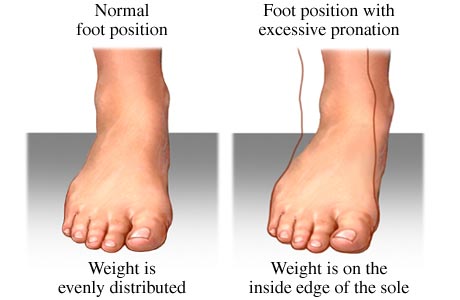
Surgical Treatment
Surgery is a last option for those with advanced and painful bunions that do not respond to any other treatment. The surgical operation to correct the deformity from a bunion is called a bunionectomy, which typically involves removing bony growth of the bunion, re-positioning ligaments and tendons, and realigning the bones of the toe joint. Surgery is usually a day procedure performed with a local anaesthetic. The bones may be stabilised in their new position with screws or pins. Hardware may even include absorbable pins that are broken down by the body after a few months. You can expect a 6 - 8 week recovery period during which crutches are usually required. Surgery is often successful but sometimes the big toe moves back to its previous deviated position. Proper footwear and orthotics reduces the chances of surgical failure.
Over-Pronation Of The Feet Cause And Treatment
When a foot over-pronates stress is unduly placed on the inside of the ankle and the knee, and over a long period of time, particularly if a person is involved in sports and running, this added stress starts to damage structures in the knee and ankle. The result is usually pain, particularly when running, which typically varies in severity. If the arch of the foot is weak, usually due to a lack of strength in supporting muscles of the foot, it can collapse over time, so people who aren?t flat footed can sometimes start to over-pronate in time. This can stress tissues on the underside of the foot, causing painful conditions like bunions (the abnormal inflammation and protrusion of the big toe?s joint) and Plantar Fasciitis (painful inflammation of connective tissues in the sole of the foot).

Causes
There are many possible causes for overpronation, but researchers have not yet determined one underlying cause. Hintermann states, Compensatory overpronation may occur for anatomical reasons, such as a tibia vara of 10 degrees or more, forefoot varus, leg length discrepancy, ligamentous laxity, or because of muscular weakness or tightness in the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles. Pronation can be influenced by sources outside of the body as well. Shoes have been shown to significantly influence pronation. Hintermann states that the same person can have different amounts of pronation just by using different running shoes. It is easily possible that the maximal ankle joint eversion movement is 31 degrees for one and 12 degrees for another running shoe.
Symptoms
In addition to problems overpronation causes in the feet, it can also create issues in the calf muscles and lower legs. The calf muscles, which attach to the heel via the Achilles tendon, can become twisted and irritated as a result of the heel rolling excessively toward the midline of the body. Over time this can lead to inflexibility of the calf muscles and the Achilles tendon, which will likely lead to another common problem in the foot and ankle complex, the inability to dorsiflex. As such, overpronation is intrinsically linked to the inability to dorsiflex.
Diagnosis
One of the easiest ways to determine if you overpronate is to look at the bottom of your shoes. Overpronation causes disproportionate wear on the inner side of the shoe. Another way to tell if you might overpronate is to have someone look at the back of your legs and feet, while you are standing. The Achilles tendon runs from the calf muscle to the heel bone, and is visible at the back of the ankle. Normally it runs in a straight line down to the heel. An indication of overpronation is if the tendon is angled to the outside of the foot, and the bone on the inner ankle appears to be more prominent than the outer anklebone. There might also be a bulge visible on the inside of the foot when standing normally. A third home diagnostic test is called the ?wet test?. Wet your foot and stand on a surface that will show an imprint, such as construction paper, or a sidewalk. You overpronate if the imprint shows a complete impression of your foot (as opposed to there being a space where your arch did not touch the ground).

Non Surgical Treatment
There are exercises that you can do to help deal with the effects and treat the cause. Obviously you can opt for an insert into your shoe either by way of your sports shop or go see a podiatrist. Like anything in your body that is not working correctly; you will have to manage your condition. Don't put off dealing with the problem as it will manifest associated issues along the alignment and as far up as your neck. If it's mild pronantion, I suggest running barefoot. If you can't do this then don't wear shoes at all at home or in the office as much as possible. Give your calf muscles a huge stretch everyday as these with the ligaments from the foot up to the muscle get tight and are linked to your pain. Loosen your calf muscles as much as possible. Great exercise is to sit barefoot with a marble on the floor in front of you. Grab the marble with your toes and try to hold it tight in the middle of the base of your foot. Ping pong balls and even golf balls work. Do this each night and combined with calf stretches you'll start to correct the muscle alignment gradually in the foot. Put more attention into massaging your feet, standing with a good posture, stretching your feet, ankles and calf muscles. Lastly, if you are fat this will not help at all. You must lose weight swimming, cycling and eradicating sugar and fat from your diet. The added strain on the foot by being a fat body compounds the problems and inhibits corrective results that you are after.
Prevention
With every step we take, we place at least half of our body weight on each foot (as we walk faster, or run, we can exert more than twice our body weight on each foot). As this amount of weight is applied to each foot there is a significant shock passed on to our body. Custom-made orthotics will absorb some of this shock, helping to protect our feet, ankles, knees, hips, and lower back.
What Are The Causes Of Calcaneal Apophysitis?
Pain in the heel of a child's foot, typically brought on by some form of injury or trauma, is sometimes Sever's Disease. The disease often mimics Achilles tendonitis, an inflammation of the tendon attached to the back of the heel. A tight Achilles tendon may contribute to Sever's Disease by pulling excessively on the growth plate of the heel bone. This condition is most common in younger children and is frequently seen in the active soccer, football or baseball player. Sport shoes with cleats are also known to aggravate the condition. Treatment includes calf muscle stretching exercises, heel cushions in the shoes, and/or anti-inflammatory medications. Consult your physician before taking any medications.
Causes
Apart from age, other factors that may contribute to developing Sever?s disease include physical activity, any form of exercise that is weight bearing through the legs or stresses the soft tissue can exacerbate the pain of the disease. External factors, for example, running on hard surfaces or wearing inappropriate shoes during sport. Overuse injury, very active children may repeatedly but subtly injure the bones, muscles and tendons of their feet and ankles. In time, the accumulated injuries cause symptoms.
Symptoms
This syndrome can occur unilaterally or bilaterally. The incidence of bilaterally is approximately 60%. Common signs and symptoms include posterior inferior heel pain (over the medial and lateral surface of the bone). Pain is usually absent when the child gets up in the morning. Increased pain with weight bearing, running or jumping (= activity-related pain). The area often feels stiff. The child may limp at the end of physical activity. Tenderness at the insertion of the tendons (= an avascular necrosis of the arthropathy). Limited ankle dorsiflexion range secondary to tightness of the Achilles tendon. Hard surfaces and poor-quality or worn-out athletic shoes contribute to increased symptoms. The pain gradually resolves with rest. Reliability or validity of methods used to obtain the ankle joint dorsiflexion or biomechanical malalignment data are not commented upon, thus reducing the quality of the data. Although pain and limping are mentioned as symptomatic traits, there have been no attempts to quantify the pain or its effect on the individual.
Diagnosis
Sever?s disease can be diagnosed based on the symptoms your child has. Your child?s doctor will conduct a physical examination by squeezing different parts of your child?s foot to see if they cause any pain. An X-ray may be used to rule out other problems, such as a broken bone or fracture.
Non Surgical Treatment
In mild cases, elevating the heel through heel lifts in the shoes and decreasing activity level may be enough to control the pain. In more severe cases, orthotic therapy to help control the motion of the heel, as well as icing, elevating, and aspirin therapy may be required to alleviate the symptoms. In those children who do not respond to either therapy mentioned above, it is sometimes necessary to place the child in a below-knee cast for a period of 4-6 weeks. It is important for both the child and parents to understand that the pain and swelling associated with this disorder should resolve once the growth plate has fused to the primary bone in the heel.
Recovery
With proper care, your child should feel better within 2 weeks to 2 months. Your child can start playing sports again only when the heel pain is gone. Your doctor will let you know when physical activity is safe.
Causes Indicators And Therapy Of An Achilles Tendon Rupture
Overview
 When a tendon ruptures it can be extremely painful and cause a disability of the foot that then subsequently causes damage to the ankle joints. The tendons in the ankle include: the peroneals (peroneus brevis, peroneus longus,) anterior tibialis, posterior tibialis, and Achilles tendon. Any of these structures can become ruptured, which is a serious condition that will typically require surgery to fix.
When a tendon ruptures it can be extremely painful and cause a disability of the foot that then subsequently causes damage to the ankle joints. The tendons in the ankle include: the peroneals (peroneus brevis, peroneus longus,) anterior tibialis, posterior tibialis, and Achilles tendon. Any of these structures can become ruptured, which is a serious condition that will typically require surgery to fix.
Causes
Often an Achilles rupture can occur spontaneously without any prodromal symptoms. Unfortunately the first "pop" or "snap" that you experience is your Achilles tendon rupture. Achilles tendon rupture most commonly occurs in the middle-aged male athlete (the weekend warrior who is engaging in a pickup game of basketball, for example). Injury often occurs during recreational sports that require bursts of jumping, pivoting, and running. Most often these are tennis, racquetball, squash, basketball, soccer, softball and badminton. Achilles rupture can happen in the following situations. You make a forceful push-off with your foot while your knee is straightened by the powerful thigh muscles. One example might be starting a foot race or jumping. You suddenly trip or stumble, and your foot is thrust in front to break a fall, forcefully over stretching the tendon. You fall from a significant height. It does appear that previous history of Achilles tendonitis results in a degenerative tendon, which can grow weak and thin with age and lack of use. Then it becomes prone to injury or rupture. Certain illnesses (such as arthritis and diabetes) and medications (such as corticosteroids and some antibiotics) can also increase the risk of rupture.
Symptoms
The most common symptom of Achilles tendonitis is a sudden surge of pain in the heel and back of the ankle at the point of injury which is often described as a snapping sensation in the heel. After the injury has occurred, patients then struggle or find it near impossible to bear any weight on the affected leg. Pain can often be most prominent first thing in the morning after the injury has been rested. Swelling and tenderness is also likely to appear in the area.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made mostly by clinical examination with a defect usually noted on visual examination and by touching the area. A simple test can be done by squeezing the back of the calf with the foot resting in the air. Normally when squeezing the muscle belly the tendon will shorten causing the foot to move in a downward position. With a rupture this squeezing effect may show no movement of the foot if it is not attached properly. A negative test does not mean there isn't some degree of rupture as some of the tendon fibers may still be attached. Sometimes x-rays, an mri, or an ultrasound can be helpful in determining the extent of the rupture.
Non Surgical Treatment
Your doctor may advise you to rest your leg and keep the tendon immobile in a plaster cast while it heals. Or you may need to have an operation to treat an Achilles tendon rupture. The treatment you have will depend on your individual circumstances, such as your age, general health and how active you are. It will also depend on whether you have partially or completely torn your tendon. If you have a partial tear, it might get better without any treatment. Ask your doctor for advice on the best treatment for you. If you need pain relief, you can take over-the-counter painkillers such as paracetamol or ibuprofen. Always read the patient information that comes with your medicine and if you have any questions, ask your pharmacist for advice. 
Surgical Treatment
There are two types of surgery to repair a ruptured Achilles tendon. In open surgery, the surgeon makes a single large incision in the back of the leg. In percutaneous surgery, the surgeon makes several small incisions rather than one large incision. In both types of surgery, the surgeon sews the tendon back together through the incision(s). Surgery may be delayed for about a week after the rupture, to let the swelling go down.